Opening a Chinese restaurant in Europe presents many opportunities and challenges. To run the restaurant…
Which One Suits Commercial Kitchens, Induction Cooking, and Traditional Heating Methods?
In commercial kitchens, induction heating technology is gradually replacing traditional heating methods with its high efficiency, intelligence, and safety, and it has become an innovative force in the field of cooking. Compared with conventional gas or electric wire heating, induction heating directly generates heat inside the pot through the principle of electromagnetic induction, which not only achieves a thermal efficiency of up to 80%-90% but also has significant advantages such as precise temperature control, rapid heating, and no open flame.
This technology not only reduces energy consumption and usage costs but also significantly improves the safety and environmental protection of cooking. However, traditional heating methods still have certain advantages in some special cooking needs (such as high-temperature stir-frying) and pot adaptability. This article will deeply explore the differences between electromagnetic heating and traditional heating methods, reveal its unique charm in modern cooking, and provide readers with practical references for choosing heating methods.
I. What is the Difference Between Induction Heating and Traditional Heating Methods?
There are significant differences between electromagnetic heating and traditional heating methods (such as gas, electric heating wire, etc.) in terms of principle, efficiency, safety, control accuracy, usage cost, environmental protection, applicability, noise, maintenance, and appearance design. The following is a detailed comparison:
1. Heating Principle
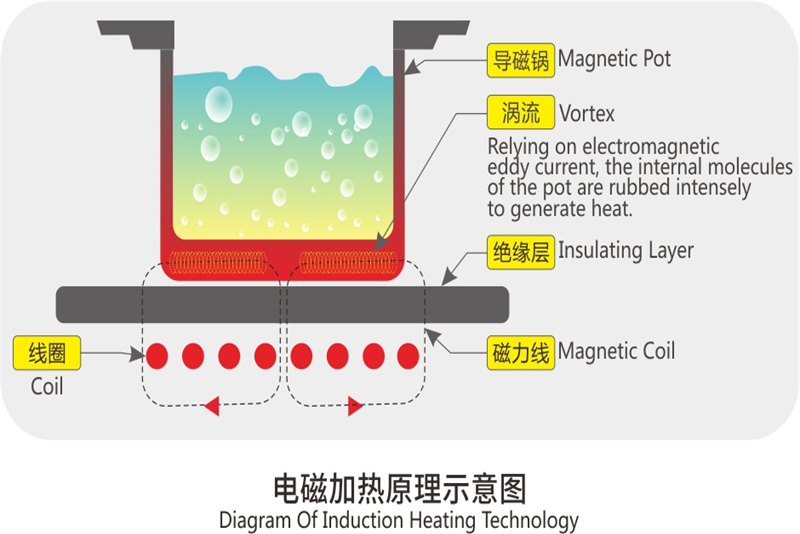
(1) Induction Heating
Through the principle of electromagnetic induction, an alternating magnetic field is used to generate eddy currents in magnetically conductive pots (such as iron pots and stainless steel pots), causing the pots to heat themselves. Heat is generated directly inside the pot, and the heating speed is fast and uniform.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: Heat is generated by burning gas (such as natural gas and liquefied gas), and the flame directly heats the bottom of the pot.
Heating wire heating: Heat is generated by passing an electric current through a resistance wire, and the heat is transferred to the pot through conduction and radiation.
2. Heating Efficiency
(1) Induction Heating
The efficiency is as high as 80%-90%, and the heat is generated directly inside the pot, reducing the loss during heat transfer.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: The efficiency is about 40%-50%, and a large amount of heat is dissipated through smoke and surrounding air.
Heating wire heating: The efficiency is about 50%-60%, and there is a large loss during heat transfer.
3. Safety
(1) Induction Heating
No open flame, avoiding the risk of fire and explosion; built-in multiple safety protections (such as overheating protection, anti-dry burning protection, anti-leakage protection, etc.).
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: There is a risk of open flame and gas leakage, which may cause fire or explosion.
Electric heating wire heating: Although there is no open flame, the surface temperature is high, it is easy to burn, and there is a risk of leakage.
4. Control Accuracy
(1) Induction Heating
Through the intelligent control system, the firepower and temperature can be accurately adjusted to achieve precise temperature control (such as ±1℃).
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: Control the firepower by adjusting the gas valve, but the accuracy is low, and the temperature control is not accurate enough.
Electric heating wire heating: Control the temperature by adjusting the power, but the response speed is slow, and the temperature control accuracy is low.
5. Cost of Use
(1) Induction Heating
High efficiency and energy saving, low long-term cost of use.
(2) Traditional heating
Gas heating: Gas prices fluctuate greatly, and the efficiency is low, so the long-term cost of use is high.
Heating wire heating: Although the price of electricity is relatively stable, the efficiency is low, and the long-term use cost is also high.
6. Environmental Protection
(1) Induction Heating
There is no combustion process, no harmful gases (such as carbon monoxide) are produced, and it is highly environmentally friendly.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: The combustion process may produce harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, which has a certain impact on the environment and health.
Heated wire heating: There is no combustion process, but pollution may be generated during the electricity production process.
7. Applicability
(1) Induction Heating
It is necessary to use magnetically conductive pots (such as iron pots and stainless steel pots), and it is not suitable for non-magnetic pots (such as glass pots and ceramic pots).
Traditional heating: There are no special requirements for the material of the pot, and it is more applicable.
8. Noise
(1) Induction Heating
It may produce a slight electromagnetic noise during operation, but it is usually within an acceptable range.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating: It may produce a slight flame sound during combustion, but the noise is relatively small.
Heating wire heating: It makes relatively little noise during operation.
9. Maintenance
(1) Induction Heating
Simple structure, easy maintenance, mainly requires regular cleaning of the surface and the heat dissipation system.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating requires regular inspection of gas pipelines and burners, and maintenance is relatively complicated.
Heating wire heating: heating wires are prone to aging and need to be replaced regularly.
10. Appearance Design
(1) Induction heating
Usually adopts a flat design, with a simple and modern appearance, and is easy to clean.
(2) Traditional Heating
Gas heating has a more traditional appearance, usually with a burner and a stove.
Wire heating has a variety of appearances but is usually not as simple as electromagnetic heating.
-
 Bärbar induktionsfritteuse för restaurang med dubbla korgar LT-TZL-B105
Bärbar induktionsfritteuse för restaurang med dubbla korgar LT-TZL-B105 -
 Induktionswokspis för restaurang med 2 brännare LT-TPA-B135
Induktionswokspis för restaurang med 2 brännare LT-TPA-B135 -
 Tabletop Induktionshäll för restaurang med 2 brännare LT-TPP-B135
Tabletop Induktionshäll för restaurang med 2 brännare LT-TPP-B135 -
 Full Glass Commercial Drop-in induktionshäll LT-QPM-C335
Full Glass Commercial Drop-in induktionshäll LT-QPM-C335 -
 Tabletop kommersiella induktionshällar 6 brännare LT-TBZ300VI-B135
Tabletop kommersiella induktionshällar 6 brännare LT-TBZ300VI-B135 -
 5000W Induktionswokhällar för restauranger LT-TAM-B505
5000W Induktionswokhällar för restauranger LT-TAM-B505 -
 Induktionshäll för restaurang 3500W LT-TPM-B535
Induktionshäll för restaurang 3500W LT-TPM-B535 -
 3500W kommersiell induktionskokare för bänkskiva LT-TPM-B135
3500W kommersiell induktionskokare för bänkskiva LT-TPM-B135 -
 Induktionshäll med 4 brännare för kommersiellt bruk 3500W LT-TBZ300IV-B135
Induktionshäll med 4 brännare för kommersiellt bruk 3500W LT-TBZ300IV-B135
II. What are the Specific Advantages of Intelligent Control Technology?
1. Digital Firepower
Through the electronically controlled automatic valve, the kilowatt of firepower can be accurately calculated according to the gas flow, and the firepower can be accurately adjusted, which improves the accuracy of cooking and simplifies the operation process.
2. Intelligent Temperature Control
It can detect the temperature in the cooking process in real time and automatically adjust the firepower through the automatic control algorithm according to the difference between the set temperature and the current temperature to ensure that the ingredients maintain a better temperature during the cooking process, lock in nutrition and deliciousness, and improve the cooking quality.
3. Human-Computer Interaction
Equipped with an intuitive and easy-to-use control panel, it supports multiple operation modes such as touch, buttons or knobs. Some high-end models also have voice interaction functions, and users can control the cooking process through voice commands, making cooking more convenient and efficient.
4. Timing Function
Equipped with a timing function, users can set the cooking time as needed. When the set time is reached, the induction cooker will automatically cut off the power or reduce the firepower to avoid overcooking or burning the ingredients, which improves the convenience of cooking and ensures the cooking effect of the ingredients.
5. Induction Heating
Adopting the principle of electromagnetic induction heating, the heating speed is fast and uniform, and the high power output can quickly increase the temperature of the pot, greatly shortening the cooking time. At the same time, electromagnetic heating avoids the problems of open flame and incomplete combustion in traditional gas stoves and improves energy utilization efficiency.
6. Intelligent Power Regulation
It can intelligently adjust the power output according to cooking needs to achieve more efficient energy utilization. Some products also have waste heat recovery functions to improve energy utilization efficiency further.
7. Diversified Cooking Modes
Support a variety of cooking modes, such as frying, boiling, stewing, steaming, etc., to meet different ingredients and cooking needs so that the catering industry can respond to various dishes more flexibly.
8. Easy to Clean and Maintain
The panel is usually made of stainless steel or tempered glass, which is resistant to high temperatures and corrosion and easy to clean and maintain. At the same time, intelligent control technology reduces the possibility of human operating errors and failures and reduces maintenance costs.
9. No Open-flame Heating
The use of no open-flame heating avoids safety hazards such as fire and explosion and does not produce harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, which ensures the air quality of the kitchen and the health of employees.
10. Multiple Safety Protections
It has multiple safety protection functions, such as overload protection, leakage protection, and automatic flameout. When the load exceeds the preset value, the induction cooker will automatically cut off the power supply; when an unexpected situation occurs during the cooking process, it can automatically turn off the flame. The leakage protection design also ensures the safety of use.
III. What are the Safety Features of the Smart Induction Cooker?
The safety features of the smart induction cooker mainly include the following aspects:
1. Overheat Protection
The induction cooker has a built-in overheat protection device, which will automatically cut off the power supply when the temperature is too high to prevent equipment damage or fire.
2. Leakage Protection
Electrical isolation and leakage protection functions are designed to ensure that users will not be electrocuted by contacting live parts during use.
3. Automatic Shutdown Function
When there is no pot contact, or dry burning occurs, the induction cooker will automatically detect and turn off the power supply to avoid fire and safety hazards.
4. Overload Protection
The induction cooker is equipped with an overload protection device, which will automatically cut off the power supply when the load exceeds the preset value to prevent electrical failure.
5. Anti-dry-burn Protection
The built-in sensor can detect whether the pot is dry-burned, and the heating function will be automatically turned off when dry burning is detected.
6. No Open-flame Heating
The induction cooker adopts no open-flame heating method, avoiding the fire and explosion risks of traditional gas stoves.
7. Multiple Safety Protections
Including overcurrent, overvoltage, Undervoltage protection, and an automatic shutdown function for improper use to ensure that the equipment automatically powers off under abnormal conditions.
8. Waterproof and Dustproof Design
The induction cooker has a certain waterproof and dustproof ability to prevent liquid or dust from entering the electrical components and affecting the safety of the equipment.
9. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Meet the requirements of electromagnetic compatibility to ensure that it will not interfere with other electronic devices.
10. Radiation Certification
Choose an induction cooker that has passed multi-national certification (such as EU CE and US FCC) to ensure that the electromagnetic radiation is within a safe range.
These safety features make the smart induction cooker more reliable during use, which can effectively reduce safety hazards such as fire and electric shock while ensuring the health and safety of users.
-
 Double Burners Commercial Induction Wok Cooker with 2 Pots LT-X400II-E108S
Double Burners Commercial Induction Wok Cooker with 2 Pots LT-X400II-E108S -
 Tilting Commercial Induction Flattop Bratt Pan for Food Industrial LT-PC150-F120
Tilting Commercial Induction Flattop Bratt Pan for Food Industrial LT-PC150-F120 -
 Dubbla wokbrännare för kommersiell induktion LT-X400Ⅱ-E108Y
Dubbla wokbrännare för kommersiell induktion LT-X400Ⅱ-E108Y -
 Restaurang Kinesisk Induktion Wok Range Med Soppvärmare LT-X400
Restaurang Kinesisk Induktion Wok Range Med Soppvärmare LT-X400 -
 Kinesisk kommersiell induktionswokspis med en brännare LT-X400
Kinesisk kommersiell induktionswokspis med en brännare LT-X400 -
 Kommersiell induktionsbrännare för wok med stor stekpanna LT-X400-D800
Kommersiell induktionsbrännare för wok med stor stekpanna LT-X400-D800 -
 Industriell köksinduktion Kwali Wok Range för en enhet till salu D900
Industriell köksinduktion Kwali Wok Range för en enhet till salu D900 -
 Kraftig kinesisk kommersiell induktionsspis Kadai D800
Kraftig kinesisk kommersiell induktionsspis Kadai D800 -
 Kommersiell induktionskokare med en brännare Kwail Wok Range D600
Kommersiell induktionskokare med en brännare Kwail Wok Range D600
IV. How does the Overheating Protection of the Smart Induction Cooker Work?
The overheat protection mechanism of the smart induction cooker mainly works in the following ways:
1. Temperature Sensor Detection
The induction cooker is equipped with a temperature sensor (such as a thermistor) to monitor the temperature inside the device in real time. These sensors are usually installed near key components (such as IGBT modules, heat sinks, or stove tops).
2. Voltage Divider Circuit and Signal Processing
The resistance of the temperature sensor changes with temperature. For example, the resistance of an NTC thermistor decreases when the temperature rises. The sensor is connected in series with a fixed resistor to form a voltage divider circuit, and the voltage signal at the voltage divider point is sent to the microcontroller for processing.
3. Microcontroller Comparison and Control
The microcontroller compares the voltage signal at the voltage divider point with the preset temperature threshold. Suppose it detects that the temperature exceeds the set safety range. In that case, the microcontroller will issue a shutdown command to cut off the heating function of the induction cooker, thereby achieving overheating protection.
4. Triggering Conditions of the Protection Mechanism
Overheat protection is usually divided into two situations:
(1) IGBT Overtemperature Protection
When the temperature of the IGBT module is too high, the sensor detects the abnormality and triggers protection.
(2) Overheat Protection of the Stove Surface
When the stove surface temperature is too high (such as dry burning or inappropriate pots), the sensor will also trigger protection.
(3) Recovery after Protection
When the temperature drops to a safe range, the induction cooker will automatically resume normal operation, or the user needs to reset it manually.
An overheat protection mechanism can effectively prevent the induction cooker from being damaged by overheating while ensuring safe use.
V. Summary
Electromagnetic heating has obvious advantages in efficiency, safety, control accuracy, environmental protection, and cost of use and is especially suitable for modern and commercial kitchens. However, traditional heating methods (such as gas) still have their unique advantages in applicability and certain special cooking needs (such as high-temperature stir-frying). The choice of heating method should be considered comprehensively based on specific needs and usage scenarios.
automatic cooking machine automatic cooking machines bbq chip fryer commercial cooking equipment commercial drop in induction cooker commercial food steamer commercial induction cooker commercial induction cooktop kommersiell induktionsfritös commercial induction fryer commercial induction hob commercial induction soup cooker Kommersiell induktionsångkokare commercial induction wok cooker commercial kitchen cookware food steamer hob induction cooker induction cookware INDUCTION FRYER induction grill induction hob iron wok kitchen equipment repair guide restaurangt equipment restaurant equipment stainless steel cookware user's guidance



This Post Has 0 Comments